Leaky ReLU Activation Function [with python code]

Leaky ReLU is the improved version of the ReLU Function. It is the most common and effective method to solve a dying ReLU problem. It adds a slight slope in the negative range to prevent the dying ReLU issue. If the input to the function x is positive then the output will be x, otherwise, the output will be ax, where a is a small magnitude (e.g. 0.01, 0.05, etc).
The mathematical representation of Leakt ReLU is,
![]()
Also Read:
- Numpy Tutorials [beginners to Intermediate]
- Softmax Activation Function in Neural Network [formula included]
- Sigmoid(Logistic) Activation Function ( with python code)
- Hyperbolic Tangent (tanh) Activation Function [with python code]
- ReLU Activation Function [with python code]
The coding logic for the leaky ReLU function is simple,
if input_value > 0:
return input_value
else:
return 0.05*input_valueA simple python function to mimic a leaky ReLU function is as follows,
def leaky_ReLU(x):
data = [max(0.05*value,value) for value in x]
return np.array(data, dtype=float)The Derivative of Leaky ReLU is,
![]()
A simple python function to mimic the derivative of leaky ReLU function is as follows,
def der_leaky_ReLU(x):
data = [1 if value>0 else 0.05 for value in x]
return np.array(data, dtype=float)Python Code
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Leaky Rectified Linear Unit (leaky ReLU) Activation Function
def leaky_ReLU(x):
data = [max(0.05*value,value) for value in x]
return np.array(data, dtype=float)
# Derivative for leaky ReLU
def der_leaky_ReLU(x):
data = [1 if value>0 else 0.05 for value in x]
return np.array(data, dtype=float)
# Generating data For Graph
x_data = np.linspace(-10,10,100)
y_data = leaky_ReLU(x_data)
dy_data = der_leaky_ReLU(x_data)
# Graph
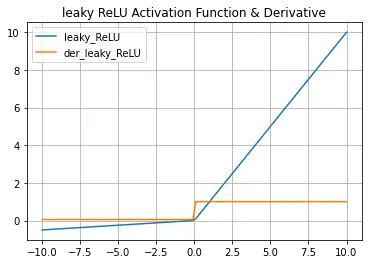
plt.plot(x_data, y_data, x_data, dy_data)
plt.title('leaky ReLU Activation Function & Derivative')
plt.legend(['leaky_ReLU','der_leaky_ReLU'])
plt.grid()
plt.show()
Post a Comment
No Comments